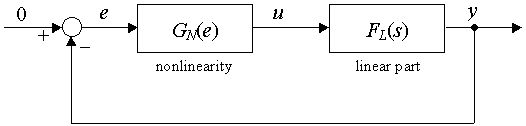
Two-Characteristics Method is a graphical (or both graphical and analytical) method for analysis of limit cycles that occur in nonlinear systems. It requires a nonlinear system composed of a high-order linear part and an isolated static nonlinearity (see the picture below). The method is also known as Harmonic Balance or Describing Function Method in literature, however, these two terms can be understood as general principles and can be used for other purposes e.g. PID controller tuning, too, while Two-Characteristics Method is restricted only to limit cycle analysis.

Two-Characteristics method is based upon describing functions and assumes following requirements to be satisfied:
For a more detailed description of the method, see literature dealing with nonlinear control systems. The Met2Char application implementing the method is available in two versions - a GUI version and a text-based version.
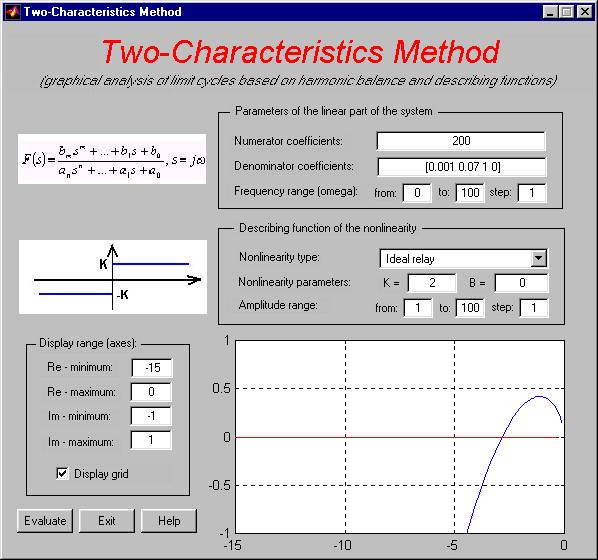
The GUI version of the Met2Char application lets user decide if there exists a limit cycle in the nonlinear system. It also allows to determine the number of limit cycles in case there are more. The harmonic balance equation is solved only graphically, for an analytical solution the text-based version has to be used. Description of GUI-controls:
Vectors of coefficients of the numerator and the denominator of the transfer function of the linear part of the nonlinear system.
Lower-bound, upper-bound and step size of the angular frequency w; these values are used in calculation and plotting of the frequency response of the linear part of the system. In complex plane the frequency response is plotted in in blue colour.
User can choose one of four possible hard nonlinearities - ideal relay, relay with dead-zone, relay with hysteresis and saturation. The parameters of the chosen nonlinearity are specified via K and B - based on these values the describing function of the nonlinearity is calculated afterwards.
Lower-bound, upper-bound and step size of the amplitude a used to calculate the describing function of the nonlinearity and to plot the nonlinearity characteristic i.e. negative reciprocal of the describing function as a function of a. In complex plane the characteristic corresponding to the nonlinearity is plotted in red colour.
Real numbers specifying the minimum and the maximum values on the real and the imaginary axes in complex plane. This range must be set appropriately according to the system which is being analyzed (different systems need different settings). Clicking the Display grid checkbox turns the grid lines in the figure on or off (similarly as MATLAB command grid on/off).
Clicking the Evaluate button starts the calculation of the two characteristics and their graphical plot in complex plane. The Exit button closes the application window. The Help button opens web-browser and displays the help file (the text you are reading) in it.
Text-based version of the Met2Char application can be found in \TextRozhr subdirectory. It is run from MATLAB Command Window by typing met2char. From the operational point of view, this version allows user to do everything that is possible to do with GUI version, besides, unlike the GUI version, it is able to solve the harmonic balance equation analytically (through Symbolic Math Toolbox) i.e. it can calculate numerical values of amplitude and frequency of the limit cycle(s). Usage example:
HARMONIC BALANCE, ANALYSIS OF LIMIT CYCLES (Two-Characteristics Method)
-------- Linear part of the system --------
Transfer function - numerator: 200
Transfer function - denominator: [1e-3 7e-2 1 0]
Transfer function:
200
------------------------
0.001 s^3 + 0.07 s^2 + s
Minimum frequency "w": 1
Maximum frequency "w": 100
Frequency step size: 1
-------------- Nonlinearity -------------
1 - ideal relay
2 - relay with dead-zone
3 - relay with hysteresis
4 - saturation
Chosen nonlinearity: 1
Relay gain: K = 2
Minimum amplitude: 1
Maximum amplitude: 100
Amplitude step size: 1
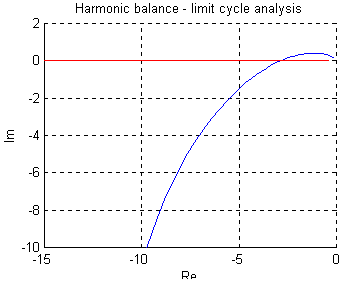
-------- Graphical solution --------
Frequency characteristic of the linear part is plotted in blue colour.
Characteristic corresponding to the nonlinearity is plotted in red colour.
The number of intersections of these two characteristics determines the number of limit cycles.
Do you want to change axes settings? (Y/N) y
Specify new settings: [Re-min, Re-max, Im-min, Im-max] = [-15 0 -10 2]
-------- Stability evaluation --------
The rule: a limit cycle is stable if the characteristic corresponding to the nonlinearity
(the red one) crosses the frequency characteristic (the blue one) from right to left
(in terms of increasing values of "w").
Beginning of the frequency characteristic: w = 1.000000, Re(Fw) = -13.959503, Im(Fw) = -199.222057
End of frequency characteristic: w = 100.000000, Re(Fw) = -0.107692, Im(Fw) = 0.138462
Beginning of the nonlinearity characteristic: A = 1.000000, Re(-1/Fa) = -0.392699, Im(-1/Fa) = 0.000000
End of the nonlinearity characteristic A = 100.000000, Re(-1/Fa) = -39.269908, Im(-1/Fa) = 0.000000
-------- Analytical solution --------
Calculated limit cycle parameters:
Amplitude: a = 7.27565, Frequency: w = 31.62278